Income Inequality or Economic Inequality is a measure of inequality in the amount of wealth or income between individuals in a given company. In its fundamental principle, it is a measure of poverty, well-being, and redistribution within tax or social systems.
We can measure income inequality with a Gini coefficient, which is a dimensionless number between 0 and 1.
- Zero means perfect income equality, where everyone has the same income.
- One means perfect inequality, one person has all the income in the state and the others have nothing.
The higher the index, the greater the income inequality in the country. Conversely, the smaller the index, the greater the income equality.
Data source:
Instructions:
Sort states by income inequality from the most balanced states to the least balanced states.
Example
Sort states by income inequality from the most balanced states to the least balanced states.
the greatest income equality (Gini the coefficient is the smallest)
- Croatia
- North Macedonia
- Czechia
the greatest income inequality (Gini the coefficient is the largest)
Solution
Sort states by income inequality from the most balanced states to the least balanced states.
the greatest income equality (Gini the coefficient is the smallest)
- Czechia 25,9
- Croatia 31,1
- North Macedonia 35,6
the greatest income inequality (Gini the coefficient is the largest)
Solve exercises
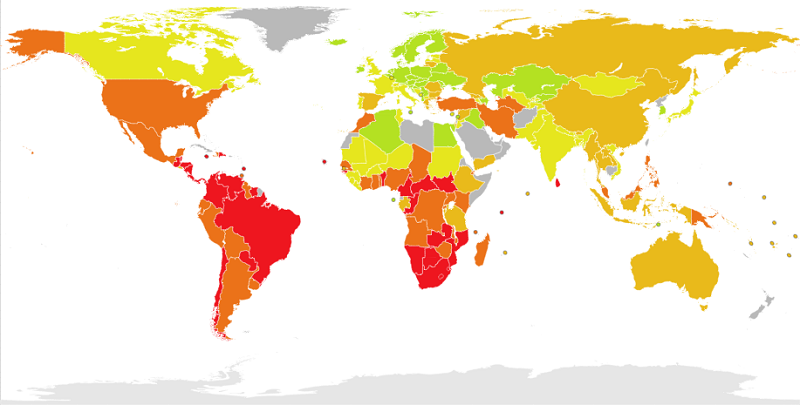
| Country | Capital city | Income iequality | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ukraine | Kiev | 25,0 | |
| 2. | Slovenia | Ljubljana | 25,4 | |
| 3. | Belarus | Minsk | 25,4 | |
| 4. | Czechia | Prague | 25,9 | |
| 5. | Moldova | Kishinev | 25,9 | |
| 6. | Slovakia | Bratislava | 26,5 | |
| 7. | Azerbaijan | Baku | 26,6 | |
| 8. | Finland | Helsinki | 27,1 | |
| 9. | Kyrgyzstan | Bishkek | 27,3 | |
| 10. | Kazakhstan | Astana | 27,5 | |
| 11. | Norway | Oslo | 27,5 | |
| 12. | Algeria | Algiers | 27,6 | |
| 13. | Belgium | Brussels | 27,7 | |
| 14. | Iceland | Reykjavík | 27,8 | |
| 15. | Netherlands | Amsterdam | 28,2 | |
| 16. | Denmark | Copenhagen | 28,2 | |
| 17. | Serbia | Belgrade | 28,5 | |
| 18. | East Timor | Dili | 28,7 | |
| 19. | Albania | Tirana | 29,0 | |
| 20. | Sweden | Stockholm | 29,2 | |
| 21. | Malta | Valletta | 29,4 | |
| 22. | Iraq | Baghdad | 29,5 | |
| 23. | Hungary | Budapest | 30,4 | |
| 24. | Austria | Vienna | 30,5 | |
| 25. | Poland | Warsaw | 30,8 | |
| 26. | São Tomé and Príncipe | São Tomé | 30,8 | |
| 27. | Croatia | Zagreb | 31,1 | |
| 28. | Korea, South | Seoul | 31,6 | |
| 29. | Germany | Berlin | 31,7 | |
| 30. | Lebanon | Beirut | 31,8 | |
| 31. | Egypt | Cairo | 31,8 | |
| 32. | Ireland | Dublin | 31,8 | |
| Country | Capital city | Income iequality | ||
| 33. | Montenegro | Podgorica | 31,9 | |
| 34. | Japan | Tokyo | 32,1 | |
| 35. | Switzerland | Bern | 32,3 | |
| 36. | Mongolia | Ulaanbaatar | 32,3 | |
| 37. | Bangladesh | Dhaka | 32,4 | |
| 38. | Mauritania | Nouakchott | 32,6 | |
| 39. | France | Paris | 32,7 | |
| 40. | Estonia | Tallinn | 32,7 | |
| 41. | Nepal | Kathmandu | 32,8 | |
| 42. | Tunisia | Tunis | 32,8 | |
| 43. | Bosnia and Herzegovina | Sarajevo | 33,0 | |
| 44. | Mali | Bamako | 33,0 | |
| 45. | United Kingdom | London | 33,2 | |
| 46. | Pakistan | Islamabad | 33,5 | |
| 47. | Armenia | Yerevan | 33,6 | |
| 48. | Guinea | Conakry | 33,7 | |
| 49. | Jordan | Amman | 33,7 | |
| 50. | Luxembourg | Luxembourg | 33,8 | |
| 51. | Cyprus | Nicosia | 34,0 | |
| 52. | Tajikistan | Dushanbe | 34,0 | |
| 53. | Sierra Leone | Freetown | 34,0 | |
| 54. | Canada | Ottawa | 34,0 | |
| 55. | Latvia | Riga | 34,2 | |
| 56. | Niger | Niamey | 34,3 | |
| 57. | Liberia | Monrovia | 35,3 | |
| 58. | Burkina Faso | Ouagadougou | 35,3 | |
| 59. | Uzbekistan | Tashkent | 35,3 | |
| 60. | Vietnam | Hanoi | 35,3 | |
| 61. | Sudan | Khartoum | 35,4 | |
| 62. | Italy | Rome | 35,4 | |
| 63. | Portugal | Lisbon | 35,5 | |
| 64. | North Macedonia | Skopje | 35,6 | |
| 65. | India | New Delhi | 35,7 | |
| Country | Capital city | Income iequality | ||
| 66. | Australia | Canberra | 35,8 | |
| 67. | Syria | Damascus | 35,8 | |
| 68. | Mauritius | Port Louis | 35,8 | |
| 69. | Romania | Bucharest | 35,9 | |
| 70. | Gambia, The | Banjul | 35,9 | |
| 71. | Greece | Athens | 36,0 | |
| 72. | Spain | Madrid | 36,2 | |
| 73. | Laos | Vientiane | 36,4 | |
| 74. | Thailand | Bangkok | 36,5 | |
| 75. | Fiji | Suva | 36,7 | |
| 76. | Yemen | Sana'á | 36,7 | |
| 77. | Kiribati | Tarawa | 37,0 | |
| 78. | Solomon Islands | Honiara | 37,1 | |
| 79. | Bulgaria | Sofia | 37,4 | |
| 80. | Bhutan | Thimphu | 37,4 | |
| 81. | Lithuania | Vilnius | 37,4 | |
| 82. | Vanuatu | Port Vila | 37,6 | |
| 83. | Tonga | Nuku'alofa | 37,6 | |
| 84. | Russia | Moscow | 37,7 | |
| 85. | Tanzania | Dodoma | 37,8 | |
| 86. | Georgia | Tbilisi | 37,9 | |
| 87. | El Salvador | San Salvador | 38,0 | |
| 88. | Gabon | Libreville | 38,0 | |
| 89. | Myanmar (Barma) | Naypyidaw | 38,1 | |
| 90. | Indonesia | Jakarta | 38,1 | |
| 91. | Maldives | Malé | 38,4 | |
| 92. | China | Beijing | 38,6 | |
| 93. | Burundi | Gitega | 38,6 | |
| 94. | Samoa | Apia | 38,7 | |
| 95. | Israel | Tel Aviv | 38,9 | |
| 96. | Tuvalu | Funafuti | 39,1 | |
| 97. | Ethiopia | Addis Ababa | 39,1 | |
| Country | Capital city | Income iequality | ||
| 98. | Uruguay | Montevideo | 39,5 | |
| 99. | Morocco | Rabat | 39,5 | |
| 100. | Iran | Tehran | 40,0 | |
| 101. | Philippines | Manila | 40,1 | |
| 102. | Micronesia | Palikir | 40,1 | |
| 103. | Trinidad and Tobago | Port of Spain | 40,3 | |
| 104. | Senegal | Dakar | 40,3 | |
| 105. | Argentina | Buenos Aires | 40,6 | |
| 106. | Turkmenistan | Ashgabat | 40,8 | |
| 107. | Kenya | Nairobi | 40,8 | |
| 108. | Malaysia | Kuala Lumpur | 41,0 | |
| 109. | Haiti | Port-au-Prince | 41,1 | |
| 110. | United States | Washington | 41,5 | |
| 111. | Ivory Coast | Yamoussoukro | 41,5 | |
| 112. | Djibouti | Djibouti | 41,6 | |
| 113. | Turkey | Ankara | 41,9 | |
| 114. | Papua New Guinea | Port Moresby | 41,9 | |
| 115. | Congo, Democratic Republic of the | Kinshasa | 42,1 | |
| 116. | Madagascar | Antananarivo | 42,6 | |
| 117. | Angola | Luanda | 42,7 | |
| 118. | Uganda | Kampala | 42,8 | |
| 119. | Nigeria | Abuja | 43,0 | |
| 120. | Togo | Lomé | 43,1 | |
| 121. | Zimbabwe | Harare | 43,2 | |
| 122. | Chad | N'Djamena | 43,3 | |
| 123. | Peru | Lima | 43,3 | |
| 124. | Mexico | Mexico City | 43,4 | |
| 125. | Ghana | Accra | 43,5 | |
| 126. | Rwanda | Kigali | 43,7 | |
| 127. | Bolivia | Sucre | 44,0 | |
| 128. | Guyana | Georgetown | 44,6 | |
| 129. | Ecuador | Quito | 44,7 | |
| 130. | Malawi | Lilongwe | 44,7 | |
| 131. | Comoros | Moroni | 45,3 | |
| Country | Capital city | Income iequality | ||
| 132. | Jamaica | Kingston | 45,5 | |
| 133. | Dominican Republic | Santo Domingo | 45,7 | |
| 134. | Nicaragua | Managua | 46,2 | |
| 135. | South Sudan | Juba | 46,3 | |
| 136. | Cameroon | Yaoundé | 46,6 | |
| 137. | Chile | Santiago | 46,6 | |
| 138. | Seychelles | Victoria | 46,8 | |
| 139. | Venezuela | Caracas | 46,9 | |
| 140. | Cape Verde | Praia | 47,2 | |
| 141. | Benin | Porto Novo | 47,8 | |
| 142. | Costa Rica | San José | 48,3 | |
| 143. | Guatemala | Guatemala City | 48,3 | |
| 144. | Paraguay | Asunción | 48,8 | |
| 145. | Congo, Republic of the | Brazzaville | 48,9 | |
| 146. | Colombia | Bogotá | 49,7 | |
| 147. | Sri Lanka | Colombo | 49,8 | |
| 148. | Panama | Panama City | 49,9 | |
| 149. | Honduras | Tegucigalpa | 50,5 | |
| 150. | Guinea-Bissau | Bissau | 50,7 | |
| 151. | Saint Lucia | Castries | 51,2 | |
| 152. | Eswatini | Mbabane | 51,5 | |
| 153. | Brazil | Brasília | 53,3 | |
| 154. | Botswana | Gaborone | 53,3 | |
| 155. | Belize | Belmopan | 53,3 | |
| 156. | Mozambique | Maputo | 54,0 | |
| 157. | Lesotho | Maseru | 54,2 | |
| 158. | Central African Republic | Bangui | 56,2 | |
| 159. | Zambia | Lusaka | 57,1 | |
| 160. | Suriname | Paramaribo | 57,6 | |
| 161. | Namibia | Windhoek | 59,1 | |
| 162. | South Africa | Pretoria | 63,0 | |
